Adversarial Training in Distillation of BERT
BERT Language Model Compression and their Robustness
In the recent years, transformer-based language learning models like BERT have been one of the most popular architectures used in the research related to natural language processing.
Productionizing these models under constrained resources to allow for the low latency the internet demands requires model compression.
While model compression has been proven to perform with similar accuracy levels and with faster inference speeds , their robustness or lack thereof is usually overlooked.
In this project we look at how we can use adversarial training either before or after model compression to preserve the robustness of the BERT Models.
This paper evaluates the performance of various models built on the ideas of adversarial training and GAN BERT finetuned on SST-2 dataset. Further the experiments in this paper seek to find evidence on whether knowledege distillation preserves robustness in the student models.
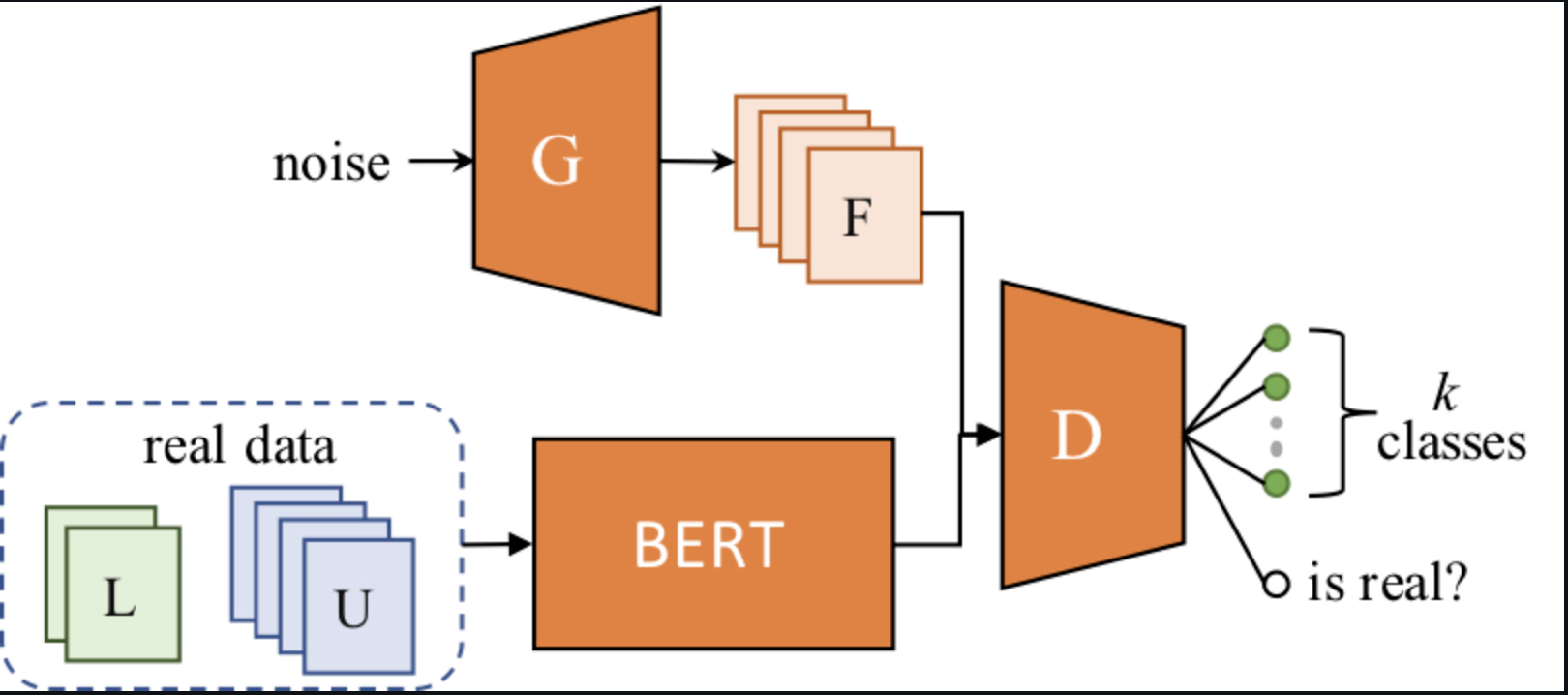


We explore two basic strategies for building robust models that are immune to adversarial attacks - Adversarial training and GAN-Bert training.
Adversarial training mainly involves the technique of data augmentation during the Fine-tuning step of the model while GAN Bert training involves self creation of perturbed examples that are included during the model training phase.
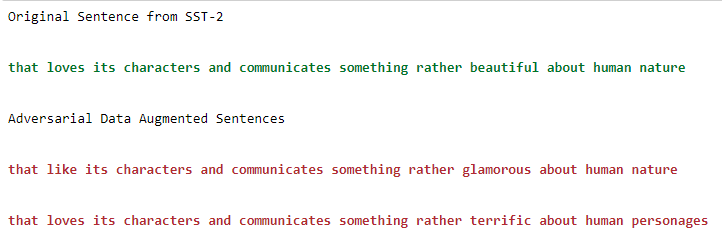
We performed Adversarial Data Augmentation using different Algorithms such as EmbeddingAugmenter , SynonymInsertionAugmenter , WordNetAugmenter. An example of adversarial data augmentation for the SST-2 datasets.
Results
Model Performance :
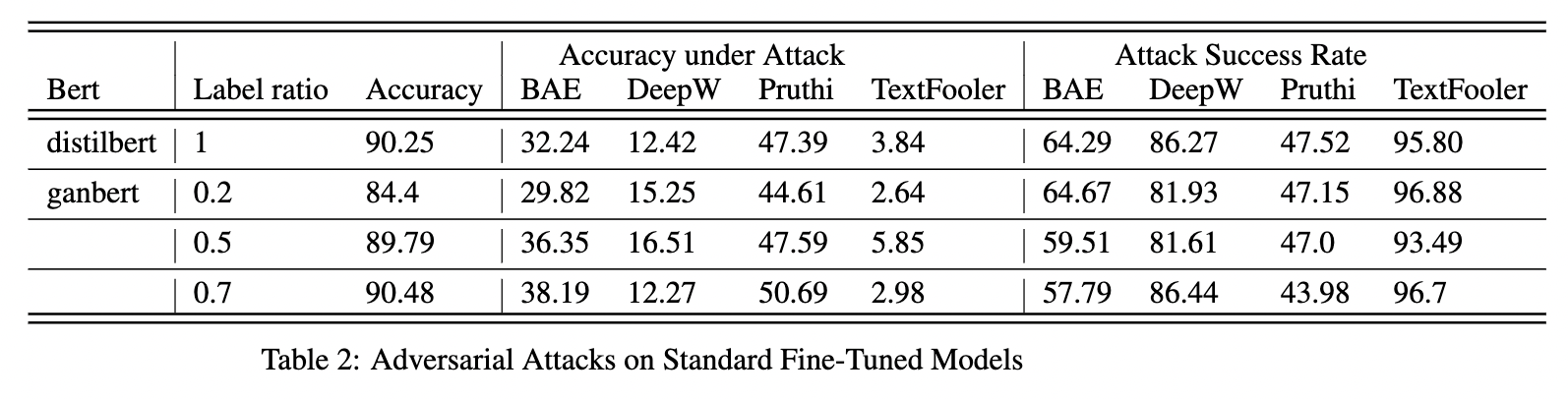
We can clearly see that the Ganbert model is able to hold itself a lot better under Attack than the finetuneed-distilbert even with just 50% of the data having labels.
This is indicative of the SSL training aiding in creating a more robust embedding space.
Attack Performance:
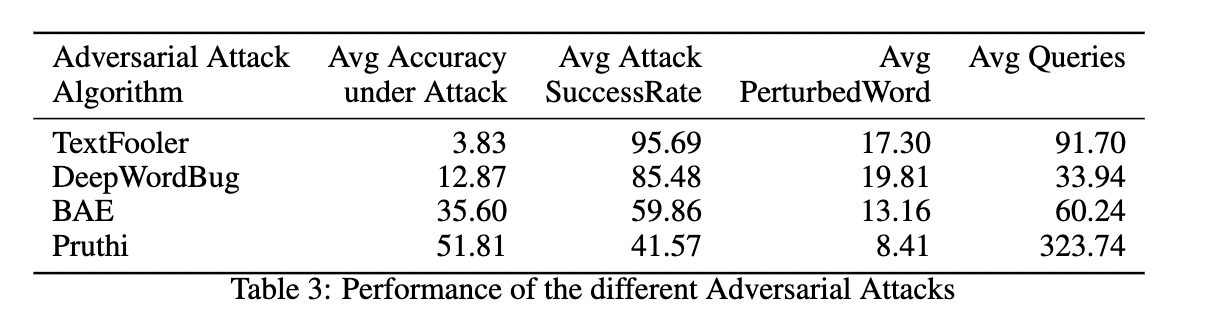
We can see that the Textfooler context-based attack out-performs visual based attacks. We can also see that the Pruthi attack which uses a Greedy Search requires a lot more queries to get the adversarial example that fools the model over the other attack algorithms.
The other 3 algorithms use a Greedy-WIR search method wherein input gradients are calculated to find the most important word in a sentence.
Attack Performed on Distilled Model.
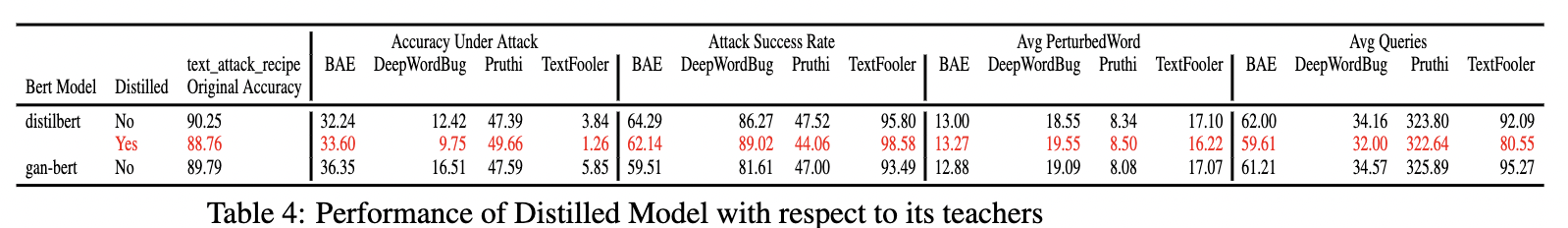
we can see that the student model performs very bad with respect to it teacher (gan-bert) and the parent distilbert from where the weights are copied.
We can see that even with half of the layers in student model , we can see that the original accuracy is very close to the teacher’s accuracy which maps with the work in DistilBert , but the drop in robustness is extremely high.
This follows our initial hypothesis that distillation does not carry robustness of the teacher onto the student and adversarial finetuning after model compression is extremely important in preserving robustness.